infrared_camera, which can be used to access and capture data from GeniCam compatible cameras.
Here, the program is used with a FLIR Systems AB-FLIR AX5-73301484 infrared camera.
Installation
Dependencies
The program has the following dependencies:
aravis (needed to stream data from the camera) https://github.com/AravisProject/aravis
libav/ffmpeg (needed to encode output videos) https://github.com/libav/libav
Compilation
Assuming the aravis library is buit and in the same folder as the infrared_camera program, the compilation command is:
gcc -O2 -Wall -Iaravis-0.7.1/src -Iaravis-0.7.1/build/src
-I/usr/include/glib-2.0 -I/usr/lib64/glib-2.0/include
-D_FILE_OFFSET_BITS=64 -Winvalid-pch
-L/home/ramin/LSW/aravis-0.7.1/build/src
-Wl,-rpath,/home/ramin/LSW/aravis-0.7.1/build/src
-laravis-0.8 -L/usr/lib64/ -lgobject-2.0 -lglib-2.0
-L/usr/lib/X11 -lX11 -lm -pthread -lavcodec -lswscale
-lavutil -lavformat
-o infrared_camera infrared_camera.c
Starting the program
The program is then called like this:
./infrared_camera config.txt
If no config file is given, a default configuration file is created.
Parameters
The default config file contains all available parameters along with their descriptions.
When the program is started, the config file is read and all parameters set.
Except for the parameter stream, all parameters can be changed during runtime by sending the parameter to STDIN.
The format is the same as in the config file, for example:
display on
turns the display on.
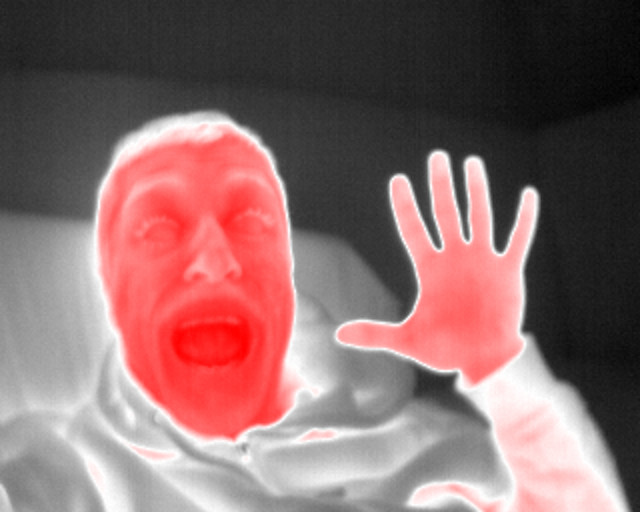
Color: It is possible to switch between 8 bit and 14 bit dynamic range of a pixel with the parameter depth, which can be 1 (8 bit) or 2 (14 bit).
14 bit images can be colored by turning on the parameter using a color palette. Several color palettes are available and accessible by the parameter pal n, where n is the number of the palette.
Videos are always colored.
The images displayed in the window are only colored when in 14 bit mode (depth 2).
In 14 bit mode, images that are saved to disk are either stored as RGB .ppm files (if image_color on) or as 16 bit grayscale .pgm files (if color off).
In 8 bit mode, the color setting is ignored and images are always saved as 8 bit .pgm files.
The size of display window can be set with the command display_zoom N, where N can be 1, 2 or 4.
The images and videos saved to disk always have the same dimensions as the sensor of the camera.
Use cases
Displaying the live camera stream
The camera stream can be displayed in an X window.
Parameters:
display ondisplay_dt TIME_IN_SECONDSdisplay_zoom N
Capturing images and saving them periodically to disk
The main task for this program is to store images of the camera periodically to disk. These are the parameters that are needed:
image_save onimage_dt TIME_IN_SECONDSimage_color onimage_pipe offimage_basename NAME
If the images are later inspected, it is helpful to acquire and store them with 14 bit (depth 2) and color enabled.
If they will be processed by another program, it is best to store them also with 14 bit, but without color.
That way, the original sensor data is kept.

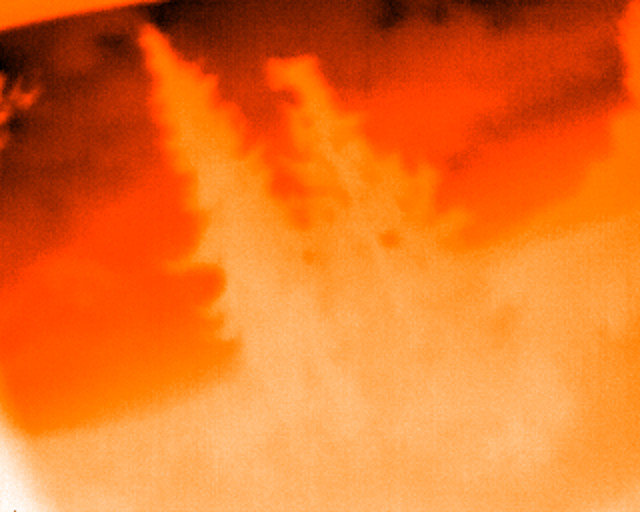
Example showing the fire palette. Here, the camera looks through a small gap at an open window to the sky. Clouds and trees are visible.
Saving the camera stream as a video
The camera stream can be stored as a compressed video. Parameters:
video_save onvideo_dt TIME_IN_SECONDSvideo_bytes_per_frame Nvideo_basename NAME
Example:
Capturing images and saving them periodically to a named pipe
Parameters needed:image_save onimage_pipe onimage_basename NAME
- First, 3 integers are sent:
- width (in this case 320)
- length (in this case 256)
- depth of a pixel (in this case 1 or 2 for 8 bit or 14 bit)
- Then, the image data are sent.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import os
import sys
import struct
def get_int(fifo):
x = fifo.read(4)
if len(x) == 0:
print("Writer closed")
return -1
return struct.unpack('i', x)[0]
FIFO = sys.argv[1]
with open(FIFO, "rb") as fifo:
while True:
w = get_int(fifo)
h = get_int(fifo)
d = get_int(fifo)
data = np.frombuffer(fifo.read(w*h*d), dtype=np.uint8)
data = np.reshape(data, (h, w))
imgplot = plt.imshow(data)
plt.pause(0.05)
plt.show()
CPU efficient image acquisition when images are saved infrequently
Whenstreaming off an image is only acquired from the camera when needed.
This would be too slow for the live view, but if images are saved every 10 minutes, for example, this saves much CPU power,
because there is no constant camera stream that needs to be read out.
Note: This mode does not work with video

